Newmanbrain, technology behind brain diagnostics
27 May 2024
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIR) allows for precise and unbiased recording of brain activity. Newmanbrain, a company born out of the Science Park at the Miguel Hernández University of Elche, uses this technique to address the lack of data in neural tools and processes, highlighting the relationship between brain activity and specific mental functions (cognitive, emotional, etc.). According to Newmanbrain’s CEO and NeurotechEU Alumni, Pablo Belmonte, the company created Theia —a portable device that measures brain activity using fNIR, protected under patent rights— to diagnose, monitor progress, and obtain feedback on treatments for patients with various neurological conditions. Additionally, Newmanbrain is a pioneering company in the Health sector, that uses Artificial Intelligence for brain diagnostics.
Newmanbrain tested Theias’s clinical efficacy in diagnosing Mild Cognitive Impairment (a precursor to Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias) through a regulated clinical trial, which has already been published (AEMPS: 1051/22/CE-R). Furthermore, Newmanbrain published a study in 2023 that exemplifies Theia fNIR’s use as the main technology for developing a methodological approach to effectively identify children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Besides this, other publications are demonstrating the applications of Theia.
Theia has four continuous wave emitters and ten detectors organized at the rectangular patch that is placed on the forehead. The device collects the recorded brain information and sends it to the cloud, where Artificial Intelligence takes place analyzing brain activity and transforming it into a report that “helps health professionals to make decisions about diagnostics”, explains Belmonte. Theia’s development makes it possible to detect —in a non-invasive way— cognitive disorders like the referred ones to aging or ADHD in children.
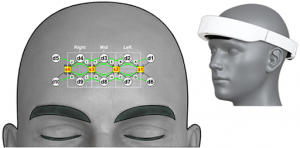
Probe geometry and placement (yellow squares = emitters; white circles = detectors), providing 16 short-channels (black lines with numbers) and 12 long-channels (green lines with letters). White dashed rectangles depict the three regions-of-interests (ROIs) explored in this work. | Source: 10.1088/1741-2552/acad2b
fNIR is an advanced technique that uses near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR). NIR is based on absorbing and reflecting infrared waves when interacting with different functional groups placed in tissues, allowing to obtain biological structures pictures, as Irene Tortos a Newmanbrain’s team member, explains. fNIR measures brain activity in real-time when detecting changes in oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin concentration. The rate of oxygen consumed by a given area of the brain is an activity indicator of the neurons in that area, so changes in the ratio between hemoglobin with and without oxygen reflect changes in neuronal activity.
When the infrared light from Theia comes into contact with brain tissue, the wave undergoes modifications that provide us with information about the composition of the sample; specifically, about changes in the metabolic activity of the neuronal tissue. This information is processed by advanced algorithms.
The Theia system aids in understanding, visualizing, and capturing the information obtained by the fNIR device. Following a session with a patient who has undergone a cognitive test, Theia’s Artificial Intelligence-based analysis platform generates a comprehensive and detailed report that healthcare professionals can use to make informed and personalized decisions about their patient’s condition.



